|
Restore in DOS environment
The latest version is v. 7, last edited on May 06, 2008
(view differences
|
view page history).
view next version >> Restoring a HD image from within a Win32 (Windows) environment is the most flexible and powerful way to restore. RSJ HD Image comes with a Win32 version of the restore program named RSJ HD Image Restore. Starting a Win32 Environment
To start an independent Windows environment, you have the following options:
We recommend the first method. A bootable USB stick or CD is quickly created using freely available tools; all you need is your Windows XP CD and a running Windows system. The result is a simple and reliable means to launch a Windows environment from USB stick or CD. The second method means you have to install Windows to a second partition, preferably on a second hard drive. If the second partition is on the same hard disk and the reason for the restore is a hard drive fail, you are back at the start... Whichever method is the better depends on the environment and your needs; both allow to run RSJ HD Image Restore and to restore a partition from CD/DVD´, local or network files, ...
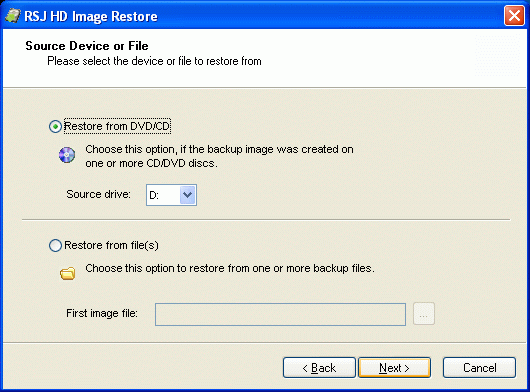
Running RSJ HD Image RestoreLaunch RSJ HD Image Restore by double clicking the file named hdrest32.exe Select the Source MediumThe backup may be located in a file with (virtually) unlimited size or on one or more CDs/DVDs, as long as they were created by RSJ HD Image Creator. Specify the source medium on the second wizard page of RSJ HD Image Restore:
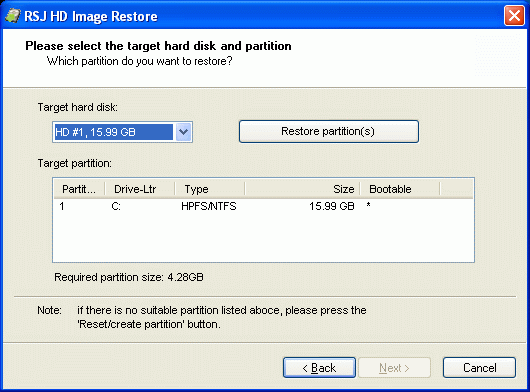
Target PartitionThe following picture is a screenshot of the target partition selection page:
If the system contains more than one hard disk, select the appropriate hard disk using the drop down list on the top left of the window. If the selected target hard disk contains partitions, they are displayed in the Target Partition table below. If there is no partition, you have the following options:
When the correct target partition is selected, press Next and Finish to confirm and restore the partition. Unattended RestoreTo run the program in unattended mode, use the following command line arguments:
|